On November 5, 2007, announced the ending of the public application ZigBee Home Automation and its availability to the public for free. With ZigBee HA offers manufacturers, system integrators, developers, etc., the option of working under a standards-based approach when introducing new products dedicated to domotics or home automation, eliminating the need to do patented technology.
This new application, defined by the own ZigBee Alliance as the new global standard for home automation, allows domotic applications developed by manufacturers are fully interoperable with each other, guaranteeing this way the end customer reliability, control, safety and comfort.
Besides the ZigBee Alliance also makes available for access the ZigBee Cluster Library, thus providing engineers and other integrators willing to work under this ideal world standard for domotic services, building blocks for applications under the common needs residential automation, thereby reducing development work and allowing more precise implementations.
For any interested in domotics and especially those that do not do any more that to think about the wireless domotics as the only solution of future, there is highly advisable the reading of this document, accessible from the page of the Zigbee Alliance, in which you will find in more detail than expected the features and capabilities that must comply with the devices, lights, scenes, HVAC devices, etc, and even the locations of each of the elements encoding. An authentic labor of abstraction that seems to indicate that the work of the Zigbee Alliance have not been paralyzed.
ZigBee turns into the necessary foundations for domotics more rational and with more common sense, low power consumption, wireless communication system (with MESH topology), his integration that allows to make nodes with little electronics, and the fact that already we have in the street the Zigbee v1.0, make it possible.
The ZigBee standard provides the network of communications, security with embedded algorithms, and support services for applications operating over the IEEE 802.15.4 layer, Control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY), and a topology network applications as varied as could be imagined, of course that the topology chosen should be the most appropriate for the final application sought.
In our case and without any doubts the topology must be of mesh (MESH), without forgetting some applications that they are forced to take into account (stars or trees), forming a hybrid topology.
The interoperability, while ZigBee is an opened standard, we must not forget that a complete definition does not exist and specifies of since developments attack with the products that we need, so it can fall into the trap of thinking that everything that goes on sale of domotics will be compatible with each of all possible developments that go out of third parties and nothing beyond of the reality, this would only happen if you had a consensus of how to behave each of the nodes designed for a specific use, and that's not going to happen, at least not at the international level, although if you will find some public profiles in the alliance(e.g. the nodes destined for lighting or HVAC...) that undoubtedly ensure compatibility between different manufacturers.
The possibility of closing private profiles can take us to systems zigbee so closed as the EIB in cable (standard course that only the supply of certain manufacturers and forced to go through this when you want to develop something), another thing is that some of the companies in the alliance start to lead certain sectors of market (something that no one has already done domotics) and if the private profile may be the roseta stone of standard use (always the issue of royalties .. but that is a lesser evil if the product has a real market penetration ... or is a standard real).
The advice is to adhere to public profiles the more possible and add only those profiles (private) of what you do not find (as long as one can pay for membership in the alliance and assign you an ID to his profile)… good strategy would be to release the code to third parties of these private profiles that we are shaping… This at least assures us that we will not be the only ones and the opening code always provided the medium / long term is a good sales strategy, well, as long as one does not want to become the MicroDOMOsoft of home automation.
The transport layer also leaves ZigBee held by the various manufacturers of chipsets for what will always be easier to develop in monochrome and be aware of who ends up outselling all your electronic chipsets and their definitions.
The safety already comes implicit in the Zigbee for what it will not give us headache to develop knowing that we can use 128-bit AES and 802.15.4, what kind of security will gather them and our decision will depend on the use of communications to be trated… DOMODESK advocate in making light transmission packages (well-balanced security ... not extreme) and allow for layers of software applications the stamp or tricks in order that our system is not a pasture of the public domain (i.e. that transfers the customer at home are at least as secure as your security door or alarm connected). The concept of "Trust Center" and key assignment in ZigBee will leave the way clear to develop insurances in Zigbee.
Needless to say which Zigbee leaves the flattened path for the subject of RF but still will have to have a mic, be it DSP, microcontroller, etc… to make it serve our cabals of system, we think the market will start to make deals chips "all in one" that will make development easier.
Zigbee is served and Ericsson (Fortress Bluetooth) have long been talk of a light Bluetooth to cope .. (do not think they have anything to do in the land of our own, home automation).
In DOMODESK were the first and last few years about this Zigbee (buzzing bees) in our DOMOLISTA and also collaborate on a project until the day of the date frustrated by political reasons, called by us OSIRIS RF, and just as in the primitive times of Bluetooth, and just as in the primitive times of Bluetooth, there is a risk of extol too without even having put feet on the ground, be cautious… at least journalists, ZigBee is a good technology for… but it is necessary that those who put to do things are also good in applying it, and it remains to be seen. Certainly, the topic of the homologation happens for the TÜV. Introduction to Zigbee.

ZigBee is an alliance, nonprofit, more than 100 companies, most of which semiconductor manufacturers, in order to facilitate the development and implementation of a low cost wireless technology.
Include companies such as Invensys, Mitsubishi, Honeywell, Philips and Motorola who work to create a standard system of communications, via radio and bidirectional, to use it inside devices of home automation, building automation (inmotics), industrial control, PC peripherals, toys, medical sensors. The members of this alliance justify the development of this standard to fill the void that occurs below the Bluetooth.
Is Zigbee valid for Domotics?
To interact remotely with all these devices, we need to work with a single standard to have them all under one network, specifically in our home. One of the most promising is ZigBee protocol based on IEEE 802.15.4. With this 'THOROUGHLY' we claim that you know that it is ZigBee, how it works and why it is one of the future of domotics worldwide ...
But until then, there have been created new wireless networks such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other upcoming WiMAX, Wireless USB, etc.. Table 1 represent a comparison of the three technologies already known and being expanded. Wireless cameras, highlighted by remote control, are an example of how to apply these technologies for domotics and control areas. But the problem is that these technologies do not satisfy the requirements of domotics, because his architecture did not think about it when they were created, and for other reasons.
| Standar | Band Width |
Power Consumption |
Benefits | Applications |
| Wi-Fi | Up to 54Mbps | Transmitting 400th, 20th to stand | High bandwidth |
Browsing the Internet, computer networks, file transfer. |
| Bluetooth | 1 Mbps | Transmitting 40th, 0’2th to stand | Interoperability, cable replacement | Wireless USB, mobile, home computing |
| ZigBee | 250 kbps | Transmitting 30th, 3th to stand | Long battery life, low cost | Remote control, battery-dependent products, sensors, toys |
Table 1: Comparison of Wireless Technologies
If we look at the kind of communications that occur in a network of sensors or actuators, we find that many of these communications are made with small data packets: to send information from a sensor (e.g. activated = detect smoke ), or simply to monitor the status of the sensors. Besides being small packets of information, most of the devices can be 'asleep' to send information (because nothing happens) and activated to detect anything. The main features of these sensors are:
The possibility of being 'asleep' for long periods of time.
Its simplicity.
Its low cost.
A home automation system must be able to control different configurations: star, bus &ldots; to cover the area of a house, and especially the MESH configuration (grid) allow us not depend upon the range.
Definitively, what is ZigBee?
ZigBee is an ideal system for home automation networks, specifically designed to replace the proliferation of sensors / actuators individual. ZigBee was created to cover the market need for a low-cost, standard for wireless networks of small packets of information, low power consumption, safe and reliable.
To implement this system, a working group made up of several industries (www.ZigBee.org), is developing the standard. The business alliance is working closely with IEEE to ensure integration, complete and operational. The ZigBee Alliance will also serve to test the devices are created with this technology. ZigBee only is the standard based on the technology necessary for the remote control of sensores/actuadores that are in use in home automation.
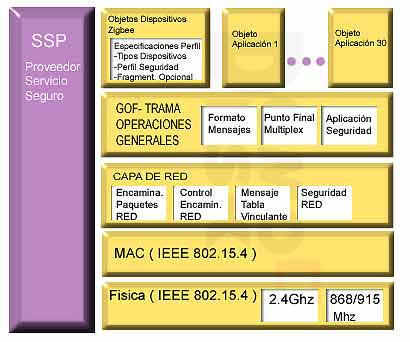
Figure 1: Architecture ZigBee Following the standard reference model OSI (Open Systems Interconnection), Figure 1 shows the structure of the layered architecture. The first two layers, the physical (PHY) and medium access (MAC), are defined by the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. The upper layers are defined by the ZigBee Alliance. The IEEE working group spent the first draft of the physical layer and media access in 2003. A final version of the network layer (NWK) ended last year, and in June 2005 we already have a public Zigbee 1.0.
ZigBee products work in a frequency band which includes the 2.4 Ghz (worldwide), 902 to 928 MHz (in the U.S.) and 866Mhz (Europe). Data transfer up to 250 Kbs can be transmitted in the 2.4GHz band (16 channels), up 40kps at 915MHz (10 channels) and in 20kps of 868Mhz (single channel). The transmission distance may vary from 10 meters to 75, depending on the transmission power and environment. As WiFi, ZigBee using DSSS (direct sequence spread spectrum) in the 2.4 GHz band. In the 868 and 900MHz bands also use direct sequence spread spectrum but with binary phase modulation.
How is this standard structure?
The following figure shows the fields of the four basic packet types: data, ACK, MAC and beacon.

Figure 2: Frames
The data packet has a data upload of up to 104 bytes. The plot is numbered to ensure that all packets arrive. A field ensures that the packet was received without errors. This structure increases reliability of transmission in difficult conditions.
Another important structure is the ACK, or acknowledgment. This frame is a feedback from the receiver to the sender, to confirm that the packet was received without errors. You can include a 'quiet time' between frames, to send a small package after each packet transmission.
The MAC packet is used for remote control and configuration of devices / nodes. A centralized network uses this type of packages to form the network distantly.
To finish, the beacon packet 'awakens' devices, listening and then return to 'sleep' if you get nothing else. These packages are important to keep all devices and nodes synchronized without having to spend a lot of battery being lit all the time.
Access to the channel. Addressing
Two channel access mechanisms are implemented in 802.15.4. For a red 'no beacon', a standard ALOHA CSMA-CA sends positive acknowledgments for correctly received packets. In a network 'with beacons' structure 'superframe' is used to control access to the channel. The superframe is studied by the network coordinator to transmit 'beacon frames' at certain intervals (every multiple of 15.38 msg as every 252 seconds). This structure guarantees dedicated bandwidth and low power consumption.
The devices are routed using 64-bits and one short optional addressing of 16 bits. The field of direction included in MAC can contain information of addressing of both origins and destinations (needed to operate point to point). This double addressing is used to prevent a failure inside.
What types of devices contains?
ZigBee has three types of devices:
The network coordinator, who always maintains control of the system. It is the most sophisticated of the types of devices, needs memory and capacity of computation.
The full function device (FFD) capable of receiving messages 802.15.4 standard. This may function as a network coordinator. Additional memory and computing capacity make it ideal for Router functions or for use in network devices acting interface with users.
The reduced function device (RFD) capacity and limited functionality (specified in the standard) to the low cost and simplicity. They are the network sensors/actuators.
What does do that it has a long period of life?
The low power consumption makes the ZigBee technology have a long life without having to recharge the device. ZigBee networks are designed to conserve power on the nodes 'slaves'. Alpha
For a long time, a device 'slave' is in 'sleep' and only 'awakens' for a fraction of a second to confirm that it is 'alive' in the network of devices. For example, the transition as 'sleep' mode 'awake' (when transmitting) takes about 15ms and the enumeration of 'slave' takes about 30ms.
ZigBee networks can use the environment 'with beacons' or 'no beacon'. The beacons are used to synchronize network devices, domotics network identifying and describing the structure of the 'superframe'. Beacon intervals are determined by the network coordinator and can range from 15msg to 4 minutes.
Mode 'without beacons' is simple: is used multiple access system in a peer to peer network nearby. It functions as a network of two paths, where each device is autonomous and can start a conversation where others can interfere. The target device can not hear the petition or the channel may be busy.
Mode 'beacon' is more advisable when the network coordinator works with a battery. The devices listen to network coordinator for the 'beacon' (sending messages to all devices, broadcast, between 0.015 and 252 seconds). A device registers to the coordinator and see if there are messages for him. If no messages, the device returns to 'sleep', awakening on a schedule established by the coordinator. Having done all the 'beacon' the same coordinator returns to 'sleep'.
What is what turns it a sure system?
The security of transmissions and data are key in ZigBee technology. ZigBee uses the security model of the subcap MAC IEEE 802.15.4, which specifies 4 safety services.
Access control - the device maintains a list of the devices 'proven' in the network. Encrypted data, with a code of 128 bits. Integration of frames to protect data from being modified by others. Sequences of refreshment, to check that the frames have been replaced by others. Network controller checks these frames refreshment and value, to see if they are the awaited ones. It depends on the final device that we believe it will be our decision to provide it with more or less safety.
What importance does acquire the Cap of Network?
The network layer (NWK) unites or separates devices through the network driver, implements security and routing frames to their respective destinations. Also, the network layer of the controller of network is responsible for creating a new network and assigning address to devices in the same.
The network layer supports multiple network configurations including star, tree, and mesh, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3: Model of ZigBee network
In the star configuration, one of the FFD-type devices assumes the role of network coordinator and is responsible for initializing and maintaining the devices on the network. All the rest devices zigbee, known with the name of final devices, 'speak' directly with the coordinator. In the configuration of mesh, the ZigBee coordinator is responsible for initializing the network and choosing the parameters of the network, but the network can be expanded through the use of ZigBee routers. Alpha
The routing algorithm uses a request-response protocol to eliminate non-optimal routes, the final network can have up to 254 nodes (probably never need so many). Using local addressing, you can configure a network of more than 65000 nodes (216).
The general operational frame (GOF) is a layer between the application and the rest of layers. The GOF usually covers several elements that are common to all devices, such as sub-addressing and routing modes and description of devices, such as device type, power, modes of 'sleep' and coordinators of each one. Using a model, the GOF specifies methods, events, and data formats that are used to construct commands and responses to them.

Figure 4: Typical layout of a ZigBee device
As shown in Figure 4, the typical ZigBee device includes a chip with a radio frequency (RF IC) with a small amount of physical layer (PHY) connected to the low power/low voltage of the microcontroller of 8-bits with peripherals, connected to an application of sensor or actuator. The pile of protocols and applications is implemented in a chip of flash memory.
 |
Motorola and Atmel already offer a group of microcontrollers for ZigBee. Chipcon is showing devices operating in the 2.4GHz band. Currently, a device with ZigBee chip can cost about 6 euros, but the price may drop to two euros if the market grows. Studies suggest that this will happen in a few years. |
What do they think Zigbee's Companies?
Many companies of the home automated environment are to that "the home automation that comes" is the wireless one... and the chosen standard is: Zigbee.
Between his principal arguments, it is that to transmit the message of control, little energy is needed very, and therefore, the batteries of domotics wireless devices with Zigbee will last more time.
ABI Research noted that the wireless sensor network market, led by ZigBee, grew ten-fold from 2007 to 2010 and exceeded 4.5 crore annual shipments in 2011. ABI Research finds smart metering to be the largest market for ZigBee in 2012 and says it will continue to be the major market growth driver as global roll outs of smart meters continue apace. ZigBee/ RF4CE use in the home environment will also be a major growth driver, said ABI.
The 6th European ZigBee Developers Conference on June 27-28, 2012 once again was evidence of the wireless standard’s attractiveness by drawing more than 150 attendees, speakers and exhibitors to Munich, Germany. In his keynote, Bob Heile, chairman of the ZigBee Alliance, updated the audience on the latest news around the ZigBee standard.
"Freescale recognizes the need to support multiple ZigBee networks and even different versions of protocols within a small area," said Bruno Baylac, director and general manager of Freescale's. "Freescale has a number of innovative ZigBee solutions and its dual-PAN feature in the Kinetis KW20 family is another great addition," said Bob Heile, chairman of the ZigBee Alliance. "With the growing demand for ZigBee Certified products, Freescale's KW20 will help meet this need."

 |
The first phone comes from the Korean manufacturer Pantech & Curitel already submitted a demo version of what will be its new mobile phone that supports the ZigBee protocol. The phone is only a prototype but have not reported when would be the official start of the device. One thing I can announce is that this technology will also revolutionize the mobile world. |
One thing is clear, before or after with ZigBee devices will be imposed on the market and will be the basis of home automation: any wiring, cheap devices, simple and fast integration, networking and sensor nodes acting in unison with one end, building automation easy to install and easy to grow. It's about time.

